crm analytics examples are at the forefront of helping businesses understand customer behaviors and refine their strategies for better results. By leveraging real-world data and advanced analysis, organizations are turning raw customer information into meaningful insights that shape smarter decision-making and fuel growth.
From tracking sales performance and customer retention to segmenting audiences and predicting churn, crm analytics examples show how diverse industries use data-driven approaches to elevate their customer relationships. With powerful metrics, innovative visualizations, and the latest tools, companies can optimize engagement, personalize communication, and boost revenue in ways that were previously out of reach.
Introduction to CRM Analytics
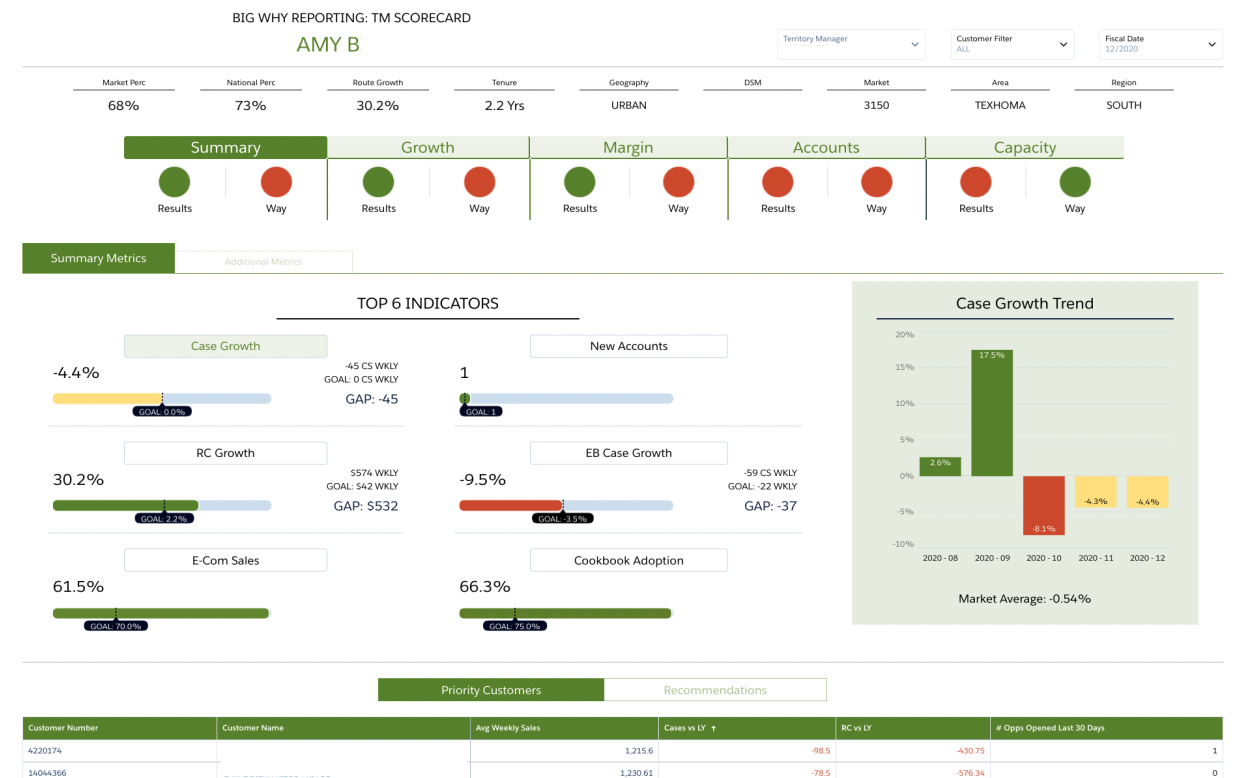
CRM analytics is a process that uses data analysis and business intelligence to transform raw customer data into actionable insights. At its core, CRM analytics enables organizations to understand customer behaviors, preferences, and engagement patterns, leading to more informed decisions and enhanced business outcomes. The significance of CRM analytics in business operations lies in its ability to drive targeted marketing efforts, optimize sales strategies, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Most CRM analytics efforts draw from a variety of data sources. These typically include customer profiles, interaction histories, sales transactions, website activities, social media engagements, and support tickets. By leveraging these data streams, companies can gain a unified view of their customers across all touchpoints.
CRM analytics plays a pivotal role in boosting customer engagement and satisfaction. By identifying trends, tracking customer journeys, and predicting future behaviors, businesses can tailor their communications, personalize offers, and proactively address customer needs. This data-driven approach not only strengthens customer loyalty but also maximizes the lifetime value of each client.
Common CRM Analytics Examples in Practice
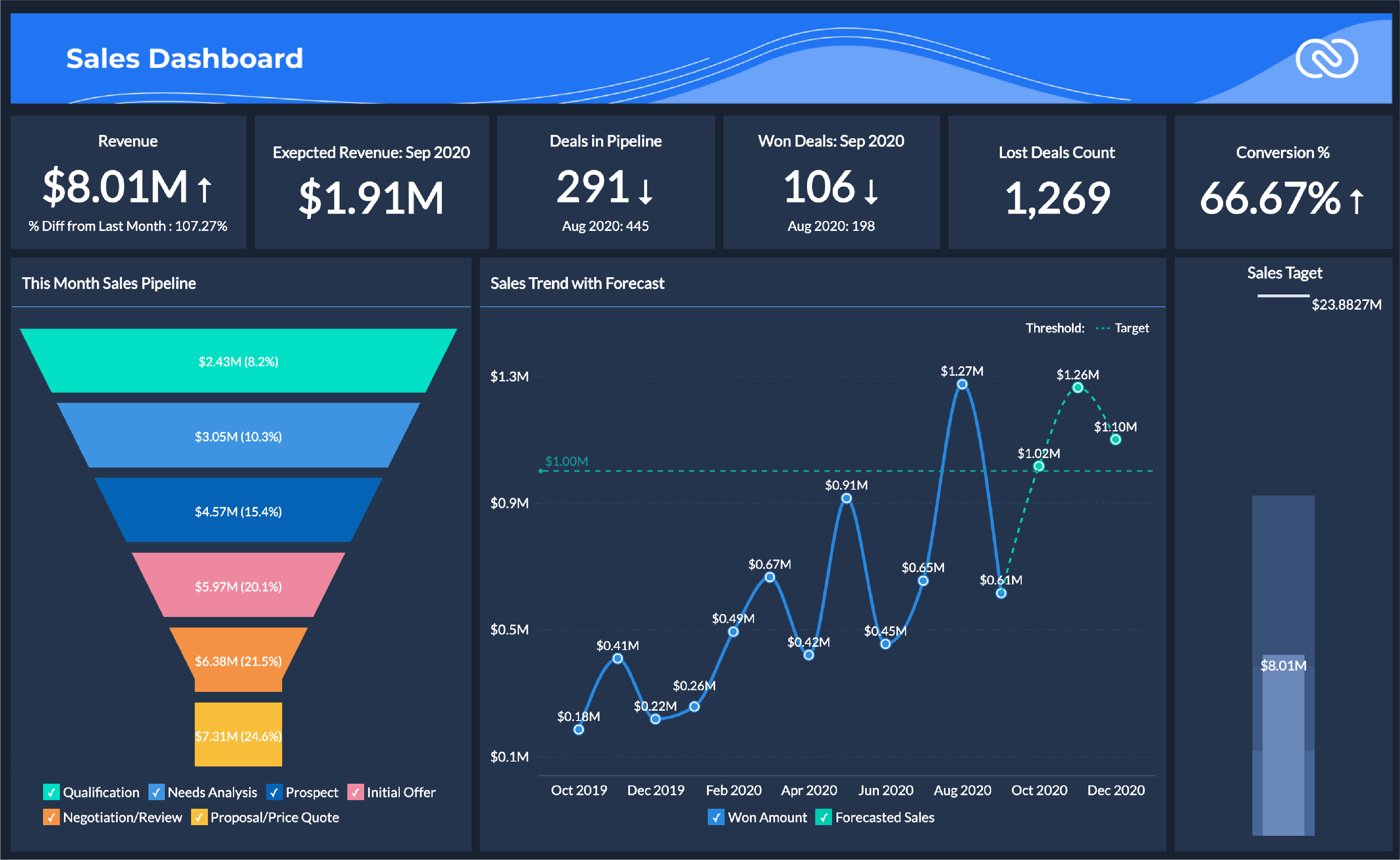
Real-world applications of CRM analytics are widespread across various industries. The table below demonstrates how different sectors leverage CRM analytics to achieve specific outcomes.
| Industry | Use Case | Metric Tracked | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Personalized Marketing Campaigns | Click-through Rate, Purchase Frequency | Boosted campaign engagement and sales |
| Banking | Churn Prediction | Customer Retention Rate | Reduced customer attrition |
| Healthcare | Patient Follow-Up Optimization | Appointment Adherence | Improved patient outcomes and loyalty |
| B2B SaaS | Lead Scoring | Lead Conversion Rate | Increased sales team efficiency |
CRM analytics is also commonly used to monitor sales performance, customer retention, and campaign effectiveness. Tracking these aspects allows businesses to identify high-performing sales reps, determine which customers are most at-risk of leaving, and evaluate which marketing initiatives yield the greatest returns.
Some of the most typical CRM analytics applications include:
- Lead Scoring – Ranking prospects based on their likelihood to convert.
- Churn Prediction – Identifying customers who are at risk of leaving.
- Customer Segmentation – Grouping customers by behavior, demographics, or value.
- Sales Forecasting – Projecting future sales based on historical data.
- Campaign Performance Analysis – Measuring the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Key Metrics and KPIs in CRM Analytics
Accurate measurement is fundamental to CRM analytics. The table below Artikels essential metrics, providing a concise view of their description, typical application, and value to the business.
| Metric Name | Description | Application | Value to Business |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | Total revenue a business can expect from a single customer account. | Forecasting, retention strategies | Guides investment in customer acquisition and retention. |
| Customer Retention Rate | Percentage of customers who remain over a period. | Loyalty programs, churn analysis | Indicates customer satisfaction and long-term business health. |
| Lead Conversion Rate | Proportion of leads converted to customers. | Sales performance evaluation | Measures sales effectiveness and campaign success. |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | Gauges customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend. | Customer satisfaction surveys | Signals brand advocacy and potential for organic growth. |
| Average Deal Size | Mean revenue per closed deal. | Sales planning, revenue forecasting | Helps set realistic targets and prioritize high-value opportunities. |
Each metric informs strategic planning and operational decisions. For example, a high CLV justifies greater investment in retention efforts, while a declining retention rate may prompt reviews of customer service quality. Lead conversion rate directly impacts sales forecasting and resource allocation, whereas NPS can serve as an early indicator of customer sentiment shifts.
The effectiveness of KPIs depends on business goals. For rapid growth, conversion rates and deal sizes may be prioritized, while mature businesses often focus on retention and CLV for sustainable profitability.
CRM Analytics Methods and Procedures
Successful CRM analytics relies on robust methods and well-defined procedures. These approaches ensure that insights derived from customer data are both reliable and actionable.
- Cohort Analysis – Tracks customer groups segmented by shared characteristics or experiences over time to identify behavioral trends.
- Predictive Modeling – Utilizes statistical algorithms and machine learning to forecast future customer actions, such as purchases or churn.
- Customer Segmentation – Divides customer base into distinct groups for targeted marketing and personalized engagement.
The step-by-step CRM analytics workflow typically involves:
- Define business objectives and analytics goals.
- Collect and integrate relevant customer data from multiple sources.
- Cleanse and preprocess the data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Apply suitable analytical methods, such as segmentation or predictive modeling.
- Interpret the results and extract actionable insights.
- Communicate findings to stakeholders using clear visualizations.
- Implement data-driven strategies and monitor their impact.
Effective CRM analytics combines business acumen with advanced data science, bringing clarity to the complex world of customer relationships.
Visualizing CRM Analytics Data
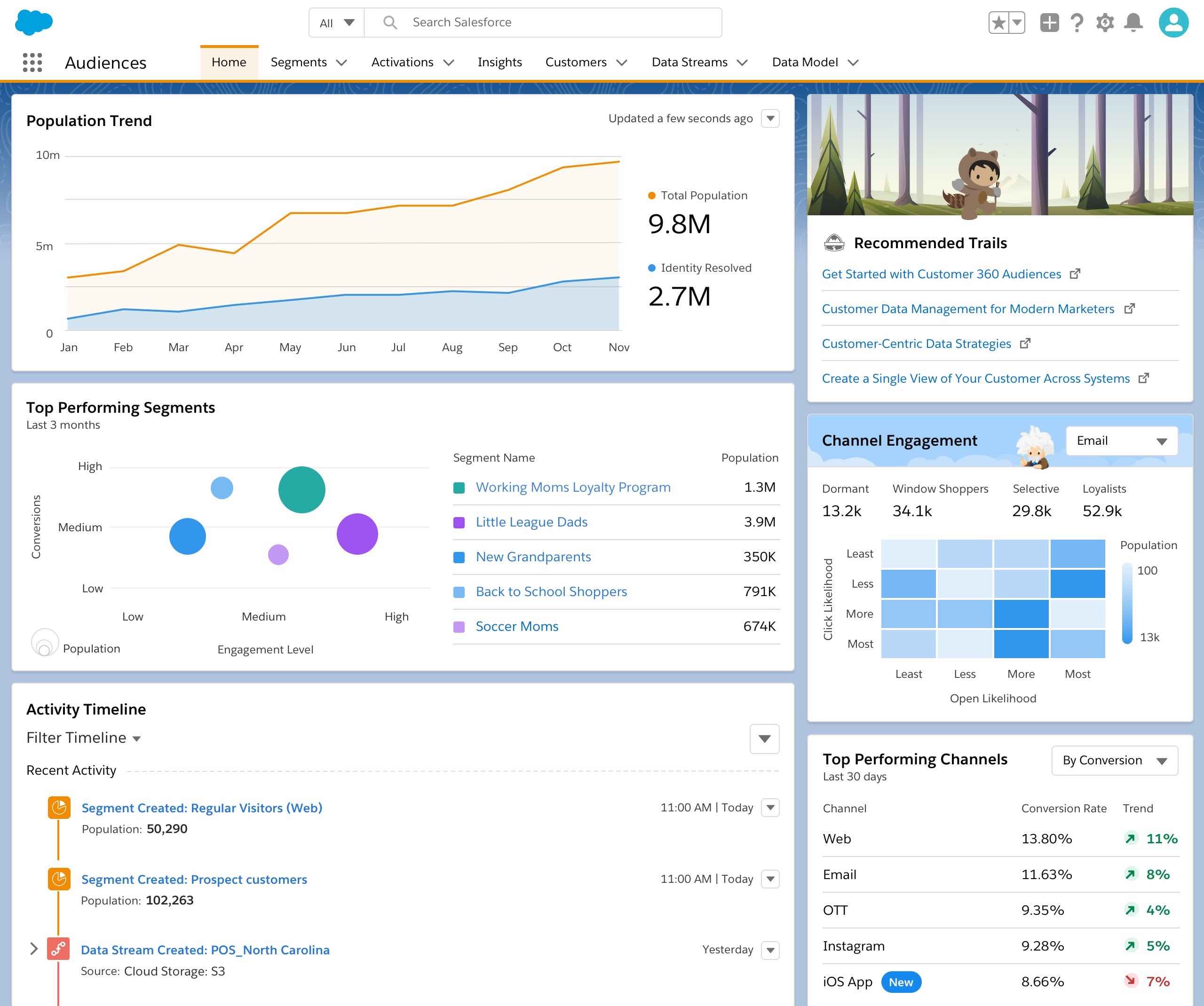
Effective visualization is crucial for communicating CRM analytics insights to decision-makers. Well-designed dashboards highlight trends, anomalies, and key KPIs, making it easier for teams to take timely and strategic actions.
The most impactful visualization types for CRM analytics include:
- Bar Charts – Ideal for comparing sales performance, customer segments, or campaign results across categories.
- Heatmaps – Useful for visualizing activity intensity, such as website clicks or support requests by time of day.
- Scatter Plots – Reveal correlations between variables, like deal size versus sales cycle length.
- Line Graphs – Track trends in metrics like retention rate or NPS over time.
- Pie Charts – Show proportional breakdowns, such as customer distribution by industry or region.
The table below summarizes visualization types, their main purposes, and illustrative insights they provide.
| Visualization Type | Main Purpose | Example Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Bar Chart | Comparing categorical data | Sales by region or product line |
| Heatmap | Identifying patterns in activity intensity | Peak website traffic periods |
| Scatter Plot | Exploring variable correlations | Relationship between customer age and retention |
| Line Graph | Monitoring trends over time | Monthly customer churn rate |
| Pie Chart | Showing part-to-whole relationships | Customer base by subscription tier |
Concluding Remarks: Crm Analytics Examples
In summary, crm analytics examples reveal a dynamic landscape where data empowers organizations to unlock new opportunities and deepen customer loyalty. As technology evolves and best practices mature, businesses that harness the full potential of CRM analytics are set to lead the way in customer-centric innovation and sustained success.
FAQ Insights
What is the main advantage of using CRM analytics examples?
The main advantage is the ability to turn customer data into actionable insights that drive better decision-making and help improve customer engagement and satisfaction.
How do crm analytics examples differ from traditional analytics?
CRM analytics specifically focus on customer data and relationship management, whereas traditional analytics may cover broader business metrics not solely related to customer interactions.
Can small businesses benefit from crm analytics examples?
Yes, small businesses can use CRM analytics to better understand their customers, streamline sales processes, and personalize marketing efforts even with limited resources.
Are specialized skills needed to use crm analytics tools?
Most modern CRM analytics tools are user-friendly and offer intuitive dashboards, but having a basic understanding of data analysis and business processes is helpful for maximizing their value.
How often should CRM analytics be reviewed?
Regularly reviewing CRM analytics—at least monthly or after major campaigns—helps businesses stay agile and responsive to changing customer needs and market trends.
